The transportation landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by technological innovation, environmental imperatives, and evolving consumer expectations. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, urban congestion, and dwindling fossil fuel reserves, electric mobility solutions have emerged as a pivotal component in shaping a sustainable future. These solutions encompass an array of technologies, infrastructures, and strategic policies designed to reduce emissions, enhance efficiency, and redefine urban mobility. This article delves into the most innovative approaches to electric mobility, exploring how they can facilitate a greener, smarter, and more resilient transportation ecosystem.
1. Electrification of Public Transit
One of the most impactful applications of electric mobility solutions lies in the electrification of public transportation. Urban buses, trams, and trains powered by electricity drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional diesel-powered fleets.
Advanced electric buses, equipped with high-capacity batteries and fast-charging systems, enable operators to maintain reliable service while lowering operational costs. Cities implementing electrified transit networks report significant reductions in air pollution, noise, and fuel dependency. The integration of smart scheduling, regenerative braking, and energy management systems further optimizes efficiency, positioning electric public transit as a cornerstone of sustainable urban mobility.
2. Electric Vehicles for Private Use
The proliferation of electric vehicles (EVs) for personal use represents a transformative shift in individual mobility. Cutting-edge battery technologies, including lithium-ion, solid-state, and next-generation graphene-based cells, have extended driving ranges while decreasing charging times.
Innovative electric mobility solutions also include modular vehicle designs and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) capabilities, allowing cars to feed electricity back into the grid during peak demand periods. This not only enhances grid stability but also encourages the adoption of EVs as dynamic energy assets rather than passive consumers. Incentivizing the transition to personal electric vehicles is essential for reducing urban emissions and achieving carbon neutrality targets.
3. Micromobility and Last-Mile Solutions
Micromobility—encompassing electric scooters, bicycles, and compact electric vehicles—addresses the critical challenge of last-mile connectivity. These solutions are particularly effective in dense urban centers where traffic congestion and parking scarcity hinder mobility.
Modern electric mobility solutions in micromobility include swappable battery systems, GPS-integrated fleet management, and AI-powered route optimization. These features enable operators to deploy vehicles efficiently, minimize downtime, and improve the user experience. By providing seamless, low-emission transportation for short trips, micromobility reduces reliance on traditional vehicles and contributes to cleaner, quieter urban environments.
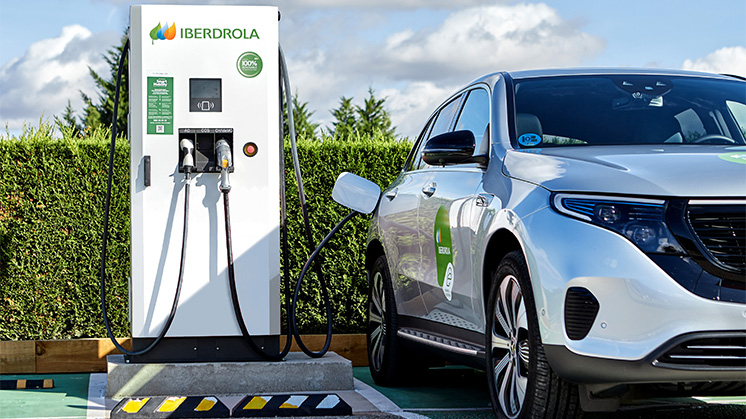
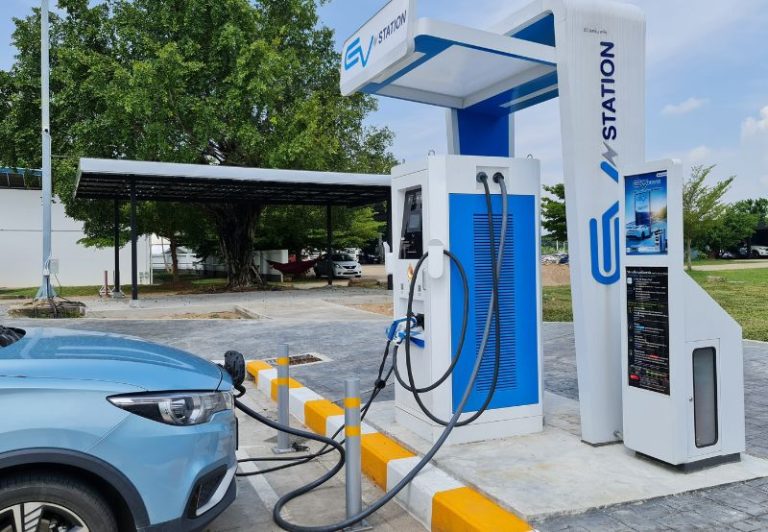
4. Charging Infrastructure and Smart Grids
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles hinges on the development of robust charging infrastructure and intelligent energy management systems. Fast-charging stations, wireless inductive charging, and distributed energy networks are essential components of this ecosystem.
Smart grids, integrated with renewable energy sources, ensure that electric mobility solutions are powered sustainably. Advanced energy storage, predictive load management, and real-time monitoring allow utilities to balance supply and demand, minimizing strain on the grid. Public-private partnerships that expand charging accessibility in urban and rural areas are crucial for accelerating EV adoption and fostering confidence among consumers.
5. Integration with Renewable Energy
To maximize environmental benefits, electric mobility solutions must be closely aligned with renewable energy generation. Solar-powered charging stations, wind-integrated energy systems, and grid-connected renewable sources enable transportation to operate with minimal carbon footprint.
Innovations in bi-directional charging allow vehicles to store surplus renewable energy and release it when needed, effectively creating a mobile energy buffer. This synergy between electric mobility and clean energy production transforms vehicles from mere transport devices into integral components of a sustainable energy infrastructure.
6. Autonomous and Connected Vehicles
The convergence of electrification with autonomy and connectivity represents a profound leap in transportation innovation. Autonomous electric vehicles (AEVs) leverage AI, machine learning, and sensor fusion to optimize driving efficiency, reduce accidents, and improve traffic flow.
Connected networks allow electric mobility solutions to communicate with each other, traffic management systems, and smart city infrastructure. This interconnected ecosystem enhances route optimization, dynamic energy distribution, and predictive maintenance, further minimizing environmental impact and operational costs. Autonomous electric fleets are poised to redefine urban mobility by combining efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
7. Commercial and Logistics Applications
The logistics sector presents significant opportunities for electric mobility solutions. Electrifying delivery vans, trucks, and cargo transport reduces emissions in a sector traditionally dominated by diesel engines.
Innovative approaches include modular electric trucks, swappable battery systems for continuous operation, and AI-driven logistics planning that minimizes energy consumption. Urban consolidation centers powered by electric fleets streamline last-mile deliveries, cutting emissions while reducing noise pollution. By transitioning commercial logistics to electric power, companies contribute meaningfully to climate goals and improve urban air quality.
8. Policy, Incentives, and Urban Planning
The success of electric mobility solutions extends beyond technology; it is also contingent upon policy frameworks, economic incentives, and forward-thinking urban planning. Governments worldwide are implementing subsidies for EV purchases, tax incentives for green fleets, and regulations that restrict fossil fuel vehicles in urban cores.
Urban planners are integrating dedicated EV lanes, micro-mobility corridors, and optimized traffic flows to support electrified transport systems. Strategic investment in infrastructure, combined with consumer incentives, accelerates adoption and ensures equitable access to sustainable mobility options. These policy interventions create an enabling environment for technological innovations to thrive.
9. Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the rapid evolution of electric mobility solutions, several challenges remain. Battery production and recycling, raw material sourcing, grid capacity, and upfront costs pose obstacles to scalability. However, advances in solid-state batteries, circular economy practices, and energy-efficient manufacturing are mitigating these concerns.
Opportunities abound in developing countries and emerging urban centers, where infrastructure is being designed with electrification in mind from the outset. Leveraging data analytics, AI, and predictive modeling enables more precise deployment of vehicles and charging infrastructure, enhancing both efficiency and environmental impact.
10. The Future of Electric Mobility
The trajectory of electric mobility solutions points toward an integrated, intelligent, and sustainable transportation ecosystem. Future developments may include ultra-fast charging networks powered exclusively by renewable energy, widespread adoption of autonomous electric public transport, and city-wide electrification of logistics.
Integration with smart cities, IoT, and AI-driven traffic management systems will optimize energy use, reduce congestion, and enhance quality of life. Moreover, societal shifts toward shared mobility, multimodal transport, and conscious consumption will reinforce the environmental and economic benefits of electrified transport. The convergence of technology, policy, and consumer behavior sets the stage for a greener, more connected future.
Innovative electric mobility solutions are central to addressing the dual imperatives of environmental sustainability and urban efficiency. By electrifying public transit, personal vehicles, micromobility options, and commercial logistics, society can dramatically reduce emissions, noise, and fossil fuel dependence.
The integration of advanced charging infrastructure, renewable energy, autonomous systems, and intelligent urban planning amplifies these benefits, creating a cohesive ecosystem that is resilient, scalable, and environmentally responsible. While challenges such as battery production, grid capacity, and equitable access remain, ongoing technological innovation and supportive policy frameworks continue to drive progress.
Ultimately, the adoption of cutting-edge electric mobility solutions represents a strategic investment in a greener, healthier, and more efficient future. By embracing electrification, cities, businesses, and individuals can contribute to a transformative shift that redefines mobility, enhances quality of life, and secures a sustainable planet for generations to come.